[This is the analysis of my preferred and most trusted economist, Michael Hudson. The implications of his analysis are so profound that I enlisted the help of Perplexity AI to evaluate it. It did, complete with the sources it used in its evaluation.]
Opponents of the war with Iran say that the war is not in American
interests, seeing that Iran does not pose any visible threat to the
United States.
This appeal to reason misses the neoconservative
logic that has guided U.S. foreign policy for more than a half century,
and which is now threatening to engulf the Middle East in the most
violent war since Korea.
That logic is so aggressive, so
repugnant to most people, so much in violation of the basic principles
of international law, the United Nations, and the U.S. Constitution,
that there is an understandable shyness in the authors of this strategy
to spell out what is at stake.
What is at stake is the U.S.
attempt to control the Middle East and its oil as a buttress of U.S.
economic power, and to prevent other countries from moving to create
their own autonomy from the U.S.-centered neoliberal order administered
by the IMF, World Bank, and other institutions to reinforce U.S.
unipolar power.
The 1970s saw much discussion about creating a New International Economic Order (NIEO). U.S. strategists saw this as a threat, and since my book Super Imperialism
ironically was used as something like a textbook by the government, I
was invited to comment on how I thought countries would break away from
U.S. control.
I was working at the Hudson Institute with
Herman Kahn, and in 1974 or 1975, he brought me to sit in on a military
strategy discussion of plans being made already at that time to possibly
overthrow Iran and break it up into ethnic parts. Herman found the
weakest spot to be Baluchistan, on Iran’s border with Pakistan. The
Kurds, Tajiks, and Turkic Azeris were others whose ethnicities were to
be played off against each other, giving U.S. diplomacy a key potential
client dictatorship to reshape both Iranian and Pakistani political
orientation if need be.
Three decades later, in 2003, General Wesley Clark pointed to Iran as being the capstone of seven countries that the United States needed to control in order to dominate the Middle East, starting with Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Libya, Somalia, and Sudan, culminating in Iran.
Most
of today’s discussion of the geopolitical dynamics of how the
international economy is changing is understandably (and rightly)
focusing on the attempt by BRICS and other countries to escape from U.S.
control by de-dollarizing their trade and investment.
But the
most active dynamic presently reshaping the international economy has
been the attempts of Donald Trump’s whirlwind presidency since January
to lock other countries into a U.S.-centered economy, by agreeing not to
focus their trade and investment on China and other states seeking
autonomy from U.S. control. (Trade with Russia is already heavily
sanctioned.)
As will be described below, the war in Iran likewise
has as an aim blocking trade with China and Russia and countering moves
away from the U.S.-centered neoliberal order.
Trump, hoping in his
own self-defeating way to rebuild U.S. industry, expected that
countries would respond to his threat to create tariff chaos by reaching
an agreement with America not to trade with China, and indeed to accept
U.S. trade and financial sanctions against it, Russia, Iran, and other
countries deemed to be a threat to the unipolar U.S. global order.
Maintaining
that order is the U.S. objective in its current fight with Iran, as
well as its fights with Russia and China – and Cuba, Venezuela, and
other countries seeking to restructure their economic policies to
recover their independence.
From the view of U.S.
strategists, the rise of China poses an existential danger to U.S.
unipolar control, both as a result of China’s industrial and trade
dominance outstripping the U.S. economy and threatening its markets and
the dollarized global financial system, and by China’s industrial socialism
providing a model that other countries might seek to emulate and/or
join with to recover the national sovereignty that has been eroded in
recent decades.
U.S. administrations and a host of U.S.
cold warriors have framed the issue as being between “democracy”
(defined as countries supporting U.S. policy as client regimes and
oligarchies) and “autocracy” (countries seeking national self-reliance
and protection from foreign trade and financial dependency).
This
framing of the international economy views not only China but any other
country seeking national autonomy as an existential threat to U.S.
unipolar domination. That attitude explains the U.S./NATO attack on
Russia that has resulted in the Ukraine war of attrition, and most
recently the U.S./Israeli war against Iran that is threatening to engulf
the whole world in U.S.-backed war.
The motivation for the attack
on Iran has nothing to do with any attempt by Iran to protect its
national sovereignty by developing an atom bomb. The basic problem is
that the United States has taken the initiative in trying to preempt
Iran and other countries from breaking away from dollar hegemony and
U.S. unipolar control.
Here’s how the neocons spell out the U.S.
national interest in overthrowing the Iranian government and bringing
about a regime change – not necessarily a secular democratic regime
change, but perhaps an extension of the ISIS/Al-Qaida Wahhabi terrorists
who have taken over Syria.
With Iran broken up and its component
parts turned into a set of client oligarchies, U.S. diplomacy can
control all Middle Eastern oil. And control of oil has been a
cornerstone of U.S. international economic power for a century, thanks
to U.S. oil companies operating internationally (not only as domestic
U.S. producers of oil and gas) and remitting economic rents extracted
from overseas to make a major contribution to the U.S. balance of
payments.
Control of Middle Eastern oil also enables the dollar
diplomacy that has seen Saudi Arabia and other OPEC countries invest
their oil revenues into the U.S. economy by accumulating vast holdings
of U.S. Treasury securities and private-sector investments.
The
United States holds OPEC countries hostage through these investments in
the U.S. economy (and in other Western economies), which can be
expropriated much as the United States grabbed $300 billion of Russia’s
monetary savings in the West in 2022. This largely explains why these
countries are afraid to act in support of the Palestinians or Iranians
in today’s conflict.
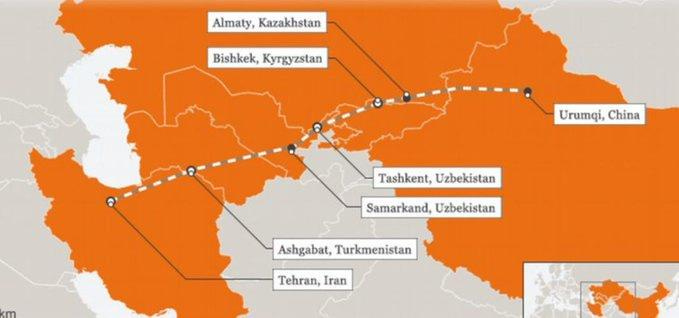
But Iran is not only the capstone to full
control of the Near East and its oil and dollar holdings. Iran is a key
link for China’s Belt and Road Initiative for a New Silk Road of railway
transport to the West.
If the United States can overthrow the
Iranian government, this interrupts the long transportation corridor
that China already has constructed and hopes to extend further west.
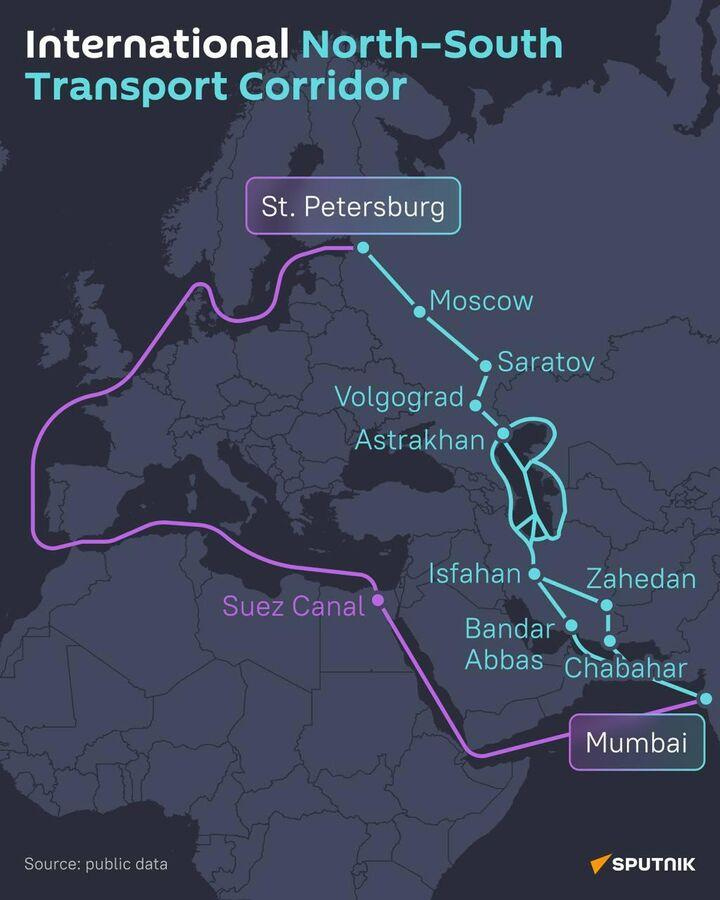
Iran
also is a key to blocking Russian trade and development via the Caspian
Sea and access to the south, bypassing the Suez Canal. And under U.S.
control, an Iranian client regime could threaten Russia from its
southern flank.
To
the neocons, all this makes Iran a central pivot on which the U.S.
national interest is based – if you define that national interest as
creating a coercive empire of client states observing dollar hegemony by
adhering to the dollarized international financial system.
I think that Trump’s warning to Tehran’s citizens to evacuate their city
is just an attempt to stir up domestic panic as a prelude to a U.S.
attempt to mobilize ethnic opposition as a means to break up Iran into
component parts. It is similar to the U.S. hopes to break up Russia and
China into regional ethnicities.
That is the U.S. strategic hope for a new international order that remains under its command.
The irony, of course, is that U.S. attempts to hold onto its fading economic empire continue to be self-defeating.
The
objective is to control other nations by threatening economic chaos.
But it is this U.S. threat of chaos that is driving other nations to
seek alternatives elsewhere. And an objective is not a strategy.
The
plan to use Netanyahu as America’s counterpart to Ukraine’s Zelensky,
demanding U.S. intervention with his willingness to fight to the last
Israeli, much as the U.S./NATO are fighting to the last Ukrainian, is a
tactic that is quite obviously at the expense of strategy.
It is a warning to the entire world to find an escape hatch.
Like
the U.S. trade and financial sanctions intended to keep other countries
dependent on U.S. markets and a dollarized international financial
system, the attempt to impose a military empire from Central Europe to
the Middle East is politically self-destructive.
It is making the
split that already is occurring between the U.S.-centered neoliberal
order and the Global Majority irreversible on moral grounds, as well as
on the grounds of simple self-preservation and economic self-interest.
The
ease with which Iranian missiles have been able to penetrate Israel’s
much-vaunted Iron Dome defense shows the folly of Trump’s pressure for
an enormous trillion-dollar subsidy to the U.S. military-industrial
complex for a similar Golden Dome boondoggle here in the United States.
So
far, the Iranians have used only their oldest and least effective
missiles. The aim is to deplete Israel’s anti-missile defenses so that
in a few weeks it will be unable to block a serious Iranian attack.
Iran
already demonstrated its ability to evade Israel’s air defenses a few
months ago, just as during Trump’s previous presidency it showed how
easily it could hit U.S. military bases.
The U.S. military budget
actually is much larger than is reported in the proposed bill before
Congress to approve Trump’s trillion-dollar subsidy.
Congress
funds its military-industrial complex (MIC) in two ways: The obvious way
is by arms purchases paid for by Congress directly. Less acknowledged
is MIC spending routed via U.S. foreign military aid to its allies –
Ukraine, Israel, Europe, South Korea, Japan, and other Asian countries –
to buy U.S. arms.
This explains why the military burden is what
normally accounts for the entire U.S. budget deficit and hence the rise
in government debt (much of it self-financed via the Federal Reserve
since 2008, to be sure).
Unsurprisingly, the international community has been unable to prevent the U.S./Israeli war against Iran.
The
United Nations Security Council is blocked by the United States’ veto,
and that of Britain and France, from taking measures against acts of
aggression by the United States and its allies.
The United
Nations is now seen to have become toothless and irrelevant as a world
organization able to enforce international law. (Its situation is much
as Stalin remarked regarding Vatican opposition, “How many troops does
the Pope have?”)
Just as the World Bank and International
Monetary Fund are instruments of U.S. foreign policy and control, so too
are many other international organizations which are dominated by the
United States and its allies, including (relevantly for today’s crisis
in West Asia) the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), that Iran
has accused of having provided Israel targeting information for its
attack on Iranian nuclear scientists and sites.
Breaking free of
the U.S. unipolar order requires a full spectrum set of alternative
international organizations independent of the United States, NATO, and
other client allies.
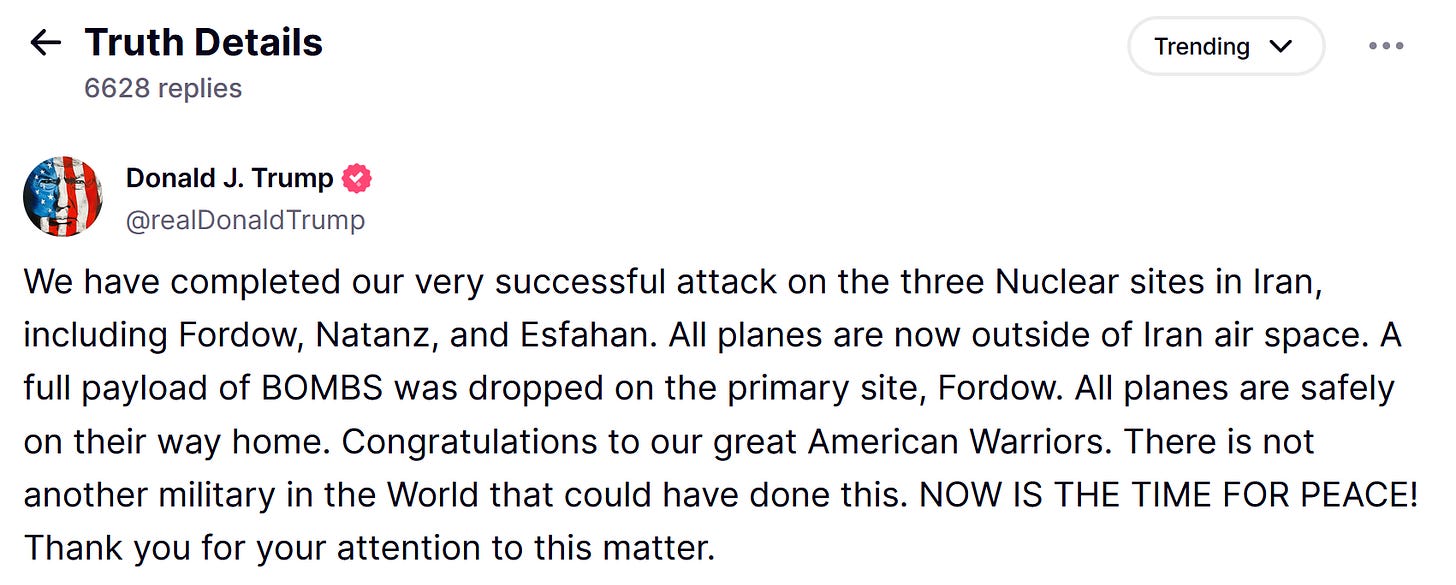
The
sound and fury of Trump’s missile attack on Iran’s most famous nuclear
sites on June 21 turned out not to be the capstone of America’s conquest
of the Middle East. But it did more than signify nothing.
Trump
must have listened to the military’s warnings that all game plans for
conflict with Iran at this time showed the United States losing badly.
His Trumpian solution was to brag on his social media account that he had won a great victory in stopping Iran’s march toward making an atom bomb.
Iran
for its part evidently was glad to cooperate with the public relations
charade. The U.S. missiles seem to have landed on mutually agreed-upon
sites that Iran had vacated for just such a diplomatic stand-down.
Trump
always announces any act as a great victory, and in a way it was, over
the hopes and goading of his most ardent neoconservative advisors. The
United States has deferred its hopes for conquest at this time.
The fight is now to be limited to Iran and Israel. And Israel already has offered to stop hostilities
if Iran does. Iran gave hope for an armistice once it has exacted due
retaliation for Israeli assassinations and terrorist acts against
civilians.
Israel is the big loser, and its ability to
serve as America’s proxy has been crippled. The devastation from Iranian
rockets has left a reported one-third of Tel Aviv and much of Haifa in
ruins.
Israel has lost not only its key military and national
security structures, but will lose much of its skilled population as it
emigrates, taking its industry with it.
By intervening on Israel’s
side by supporting its genocide, the United States has turned most of
the UN’s Global Majority against it.
Washignton’s ill-thought
backing of the reckless Netanyahu has catalyzed the drive by other
countries to speed their way out of the U.S. diplomatic, economic, and
military orbit.
So America’s Oil War against Iran can now be added
to the long list of wars that the United States has lost since the
Korean and Vietnam wars, Afghanistan, Iraq, and the rest of its
adventures leading up to its imminent loss in Ukraine. Its victories
have been against Grenada and German industry – its own imperial
“backyard,” so to speak.